
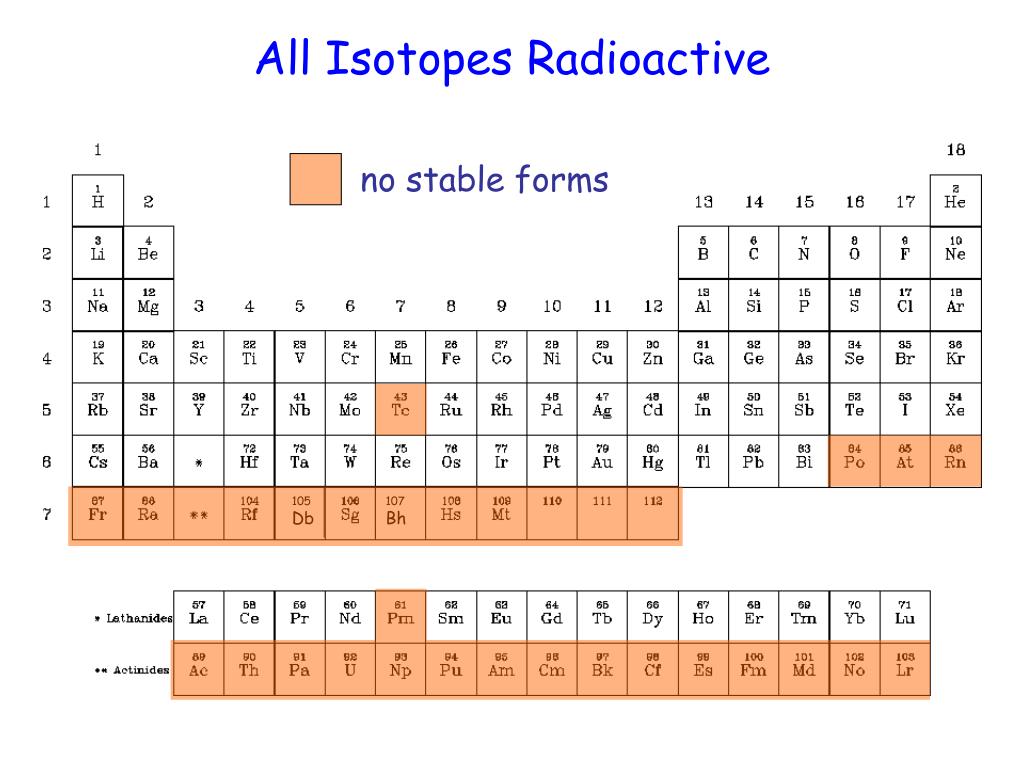
↑↓ Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties
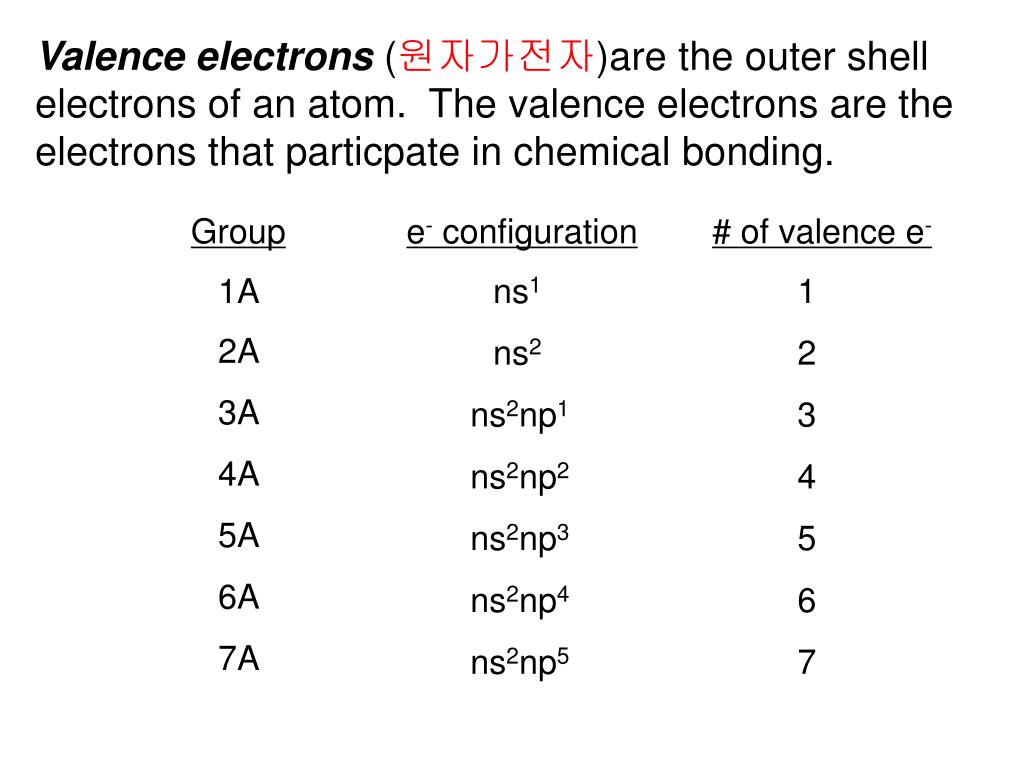
Iv) Electron spin quantum number, ms: Electrons act as though they have an intrinsic spin which gives them a magnetic moment Thus, unpaired electrons are acted on by magnetic fields and are said to be paramagnetic substances that are unaffected by magnetic fields are said to be diamagnetic The two possible spin values for an electron are a consequence of the electron spin quantum number ms where ms =± ½ These spins are often labeled “up” (↑ ↑) and “down” (↓ ↓) (although this is actually incorrect electron spin doesn’t depend on coordinates!) A maximum of 2 electrons can occupy each electron orbital, and then, only when their spins are paired: This quantum number determines the number of orbitals of shape ℓ and energy n = (2ℓ + 1)ħ Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties
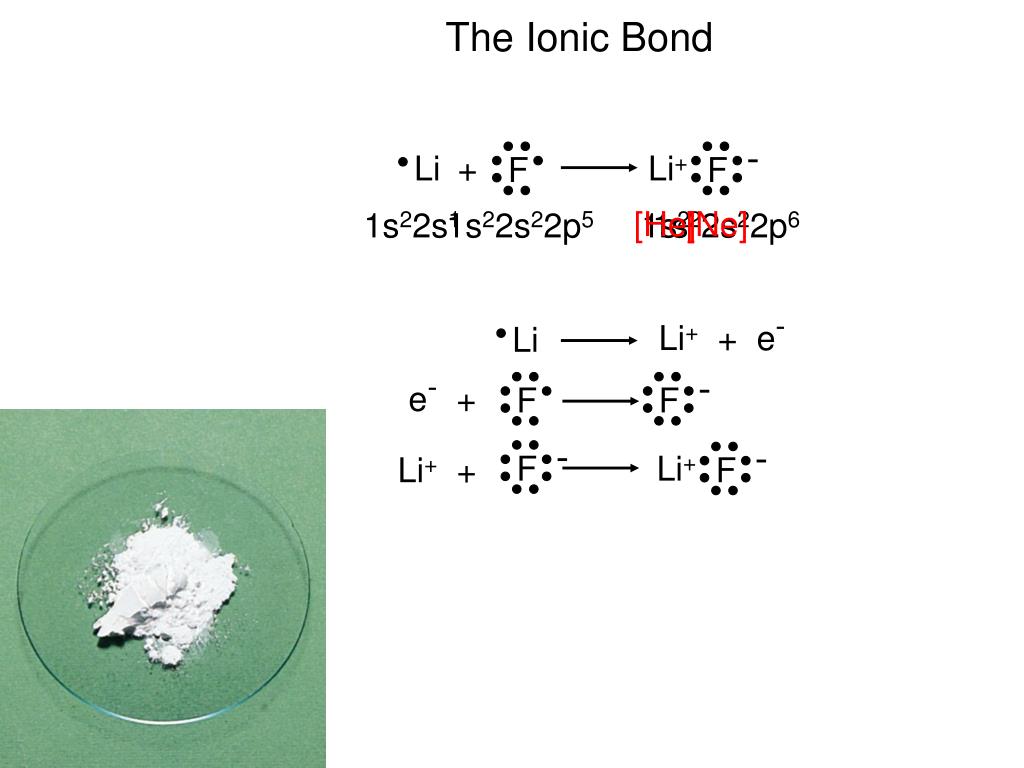
Iii) Magnetic quantum number mℓ: mℓ = -ℓ, …,0, …+ℓ in integer steps. This quantum number determines the energy of the orbital ii) Angular momentum quantum number, ℓ: ℓ = 0, 1, 2, …., n-1 This quantum number determines the shape of various orbitals having the energy of quantum number n Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties C020Įlectronic Structure and Periodic PropertiesĮlectron Orbitals ¾The properties of elements result from the electronic structure of the atom ❮ach electron in an tom is in an orbital of fixed energy that is the orbitals are said to be quantized ❮ach electron is described by 3 quantum numbers i) Principle quantum number n: n = 1,2,3, ….


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
